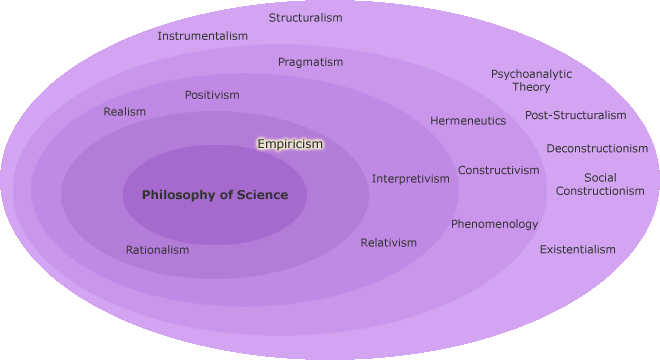
Empiricism
Empiricism views observation and experience as the bases of the formation of knowledge.
- The processes of doing research and forming knowledge are guided by sensory perceptions of the researched phenomenon, and generalisation of knowledge obtained through observations and experiences.
- You can apply the acquired knowledge to other phenomena.
- Throughout the history of science, variations of empiricism have developed.
Empiricism and rationalism are fundamental principles of the philosophy of science.
Links to more information:
Empiricism. New World Encyclopedia.
Empiricism. Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia.
Ward, Teddy. Empiricism. East Carolina University.
See what is written in Strategies on empirical research.